In the rapidly evolving world of energy storage, there’s a growing trend towards lithium-ion batteries. However, lead-acid battery manufacturers are countering this movement by introducing Thin Plate Pure Lead batteries (TPPL), an offshoot of the Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) technology. But is it fair to compare the two?
What Are TPPL Batteries?
TPPL stands for Thin Plate Pure Lead batteries, which are a relatively new type of Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) batteries. AGM batteries have been around for a while, and TPPL batteries share some similarities with them. However, there are key distinctions between the two.
One crucial difference is the rate of charge. TPPL batteries can absorb charge at a faster rate compared to standard AGM batteries, resulting in a higher but declining acceptance rate. This means TPPL batteries can charge quickly up to 70-80% but take significantly longer to reach full charge.
Lithium Battery Performance vs TPPL Battery Performance
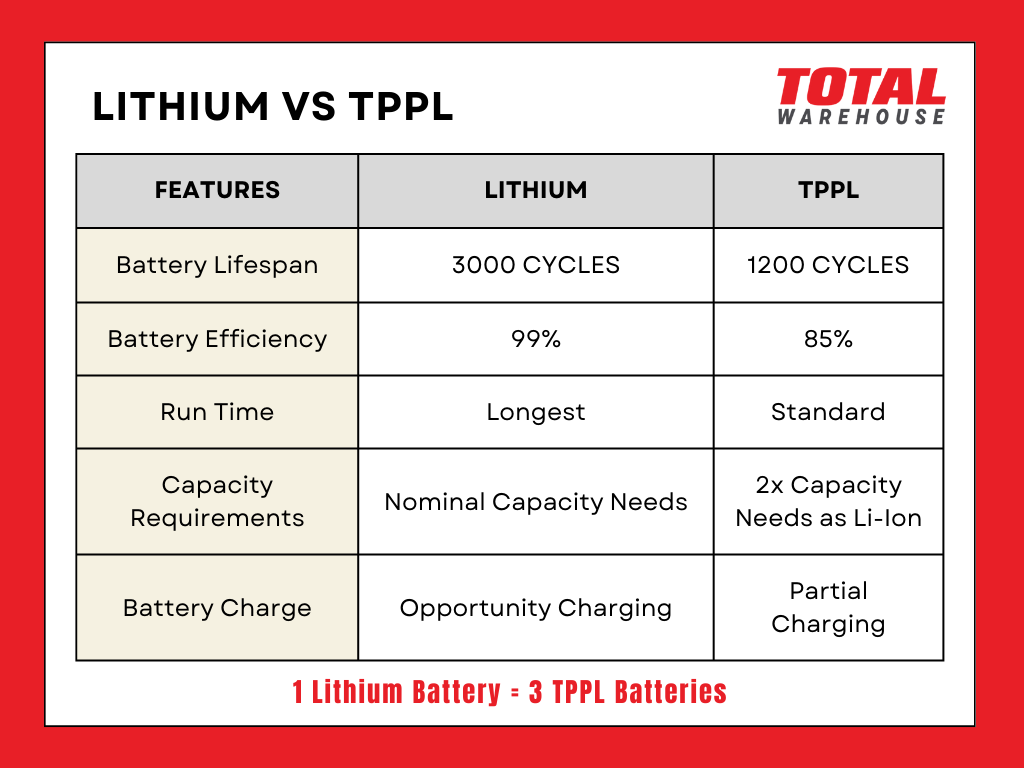
Comparing TPPL batteries to lithium-ion batteries reveals a notable difference. TPPL batteries typically require double the nominal capacity to perform the same job as lithium-ion batteries. Additionally, TPPL batteries cannot be discharged below 40% state of charge without risking damage or voiding the warranty, a limitation not present in lithium-ion batteries.
The high rate of charge and discharge in TPPL batteries results in increased internal heat, potentially reducing their lifespan. Even with proper care, TPPL batteries generally have a shorter life expectancy compared to most lithium-ion batteries, which are often measured in cycles.
Unlike lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries do not lose capacity when used at a partial state of charge, thanks to the absence of a memory effect.
Although TPPL batteries may outperform traditional lead-acid batteries in terms of efficiency, capacity, and lifespan, they still fall short of a lithium-ion battery in all category.
Performance Claims of TPPL Battery
Manufacturers have made various performance claims about TPPL batteries, with some touting their increased charging rates. Some claim that TPPL batteries can be charged up to 6 times their rated capacity, even going from completely dead to full charge in under 30 minutes. However, testing has shown that this rapid charging rate is short-lived, slowing down significantly as the battery reaches around 70% charge.
Charge capacity is another aspect where TPPL batteries behave similarly to AGM batteries when used in a partially charged state, leading to potential loss of charge capacity (memory effect). Modifying the charge capacity requires special equipment and can result in venting of electrolytes or acid fumes.
Manufacturers also claim high usable capacity, with up to 80% capacity usable for up to 1200 cycles. In contrast, lithium-ion batteries offer more than 80% usable capacity at 3000-plus cycles, depending on charging habits and application. The memory effect in TPPL batteries can reduce their capacity to around 50%.
Storage is one area where TPPL batteries do excel, with their low self-discharge rates allowing them to be stored for several months without losing charge. Some lithium-ion batteries have on-off buttons for extended storage.
Overall Thoughts on the Differences Between a Lithium-Ion Battery and TPPL Battery
After considering these differences between lithium-ion and TPPL batteries, it becomes clear that comparing them is not entirely fair. While they share the “no-maintenance” feature, they are fundamentally different technologies. Each has its own strengths and limitations, making them suitable for different applications and user needs.
At Total Warehouse, we’ve helped countless businesses across the United States achieve lower maintenance, reduced costs, increased worker satisfaction, and increased economic sustainability by making the switch. Our team of highly knowledgeable experts can help you make the right decision for your business. Give us a call at 833-868-2500 or contact us online.







